An organization’s sales team structure might be crucial to its success in the fiercely competitive world of business. Having the appropriate amount of salespeople on the floor is only one aspect of an effective sales team structure; another is developing a system that optimizes income, simplifies processes, and synchronizes sales initiatives with the company’s strategic goals.
We’ll explore what makes a sales team structure effective in this blog article, along with a suggested structure that contemporary, dynamic firms may use to leverage both conventional and cutting-edge sales strategies.
Table of Contents
- Importance of an efficient sales team structure
- Understanding different sales team structures
- Key elements of a successful sales team framework
- Sample sales team structure: Hybrid model
- Designing the most efficient sales team structure
- Implementing the structure
Importance of an efficient sales team structure
The way a sales staff is organized may have a big influence on how well the company meets its revenue targets and maintains growth over time. A carefully designed sales team structure makes ensuring that sales activities are in line with the company’s strategic goals, fosters cooperation, and makes the most of individual capabilities. Additionally, it facilitates operational simplification and raises the general effectiveness of the sales process.
Understanding different sales team structures
With time, sales team structures have changed from conventional models to more contemporary ones that take into account the shifting customer and market dynamics.
Traditional models
- Geographic division: To efficiently serve local markets, sales teams are split up according to their respective geographic regions.
- Product or service line: Groups are set up according to certain goods or services, which enables more specialized expertise and better product-specific marketing strategies.
- Market or industry sector: By utilizing knowledge in certain areas, sales efforts are concentrated on particular market segments or industries.
Modern structures
- Account-based frameworks: Sales teams concentrate on specific accounts or clients, adjusting their approach to meet the unique requirements and prospects of each.
- Inbound vs. outbound teams: Teams that manage incoming leads (inbound) or actively seek new clients (outbound) should be distinguished from one another.
- Hybrid models: Adapted to the demands of the organization, a blend of several structures is used to maximize their benefits.

Key elements of a successful sales team framework
The cornerstones of a successful sales team architecture include clearly defined duties, systems of support, and an emphasis on enduring client connections. Every element is vital to the success of sales and the expansion of the company.
Leadership roles
- Sales director: Responsible for overseeing the sales strategy, aligning it with the company’s broader objectives, and steering the sales team towards achieving these goals.
- Sales managers: Tasked with the day-to-day management of specific sales teams (like inbound or outbound), focusing on operational efficiency, mentoring, and team performance.
Core sales units
- Inbound sales team: Dedicated to managing incoming queries and leads, guiding potential customers through the sales funnel towards a successful closure.
- Outbound sales team: Engages in proactive outreach to uncover new leads and opportunities, using strategies like cold calling, email campaigns, and networking.
- Account executives: Charged with sealing the deal, these team members handle negotiations, close sales, and manage client accounts post-sale to ensure satisfaction and loyalty.
- Business development representatives (BDRs): Focus on the early stages of the sales process, identifying potential leads, qualifying them, and setting up meetings for the Account Executives.
Supportive and specialist functions
- Sales enablement: Provides the sales team with the necessary training, tools, and resources to enhance their sales techniques and effectiveness.
- Sales operations: Focuses on the optimization of sales processes and the management of sales data to ensure operational excellence and support strategic decision-making.
- Customer success team: Plays a pivotal role in maintaining and enhancing customer relationships post-purchase, aiming for high satisfaction rates and exploring opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Technological infrastructure
- The adoption of CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems, alongside other communication and productivity tools, is essential to streamline the sales process, improve team coordination, and monitor performance metrics.
This structured approach not only clarifies roles and responsibilities within the team but also ensures that each segment of the sales process is addressed, from lead generation to customer retention, creating a cohesive and effective sales operation.

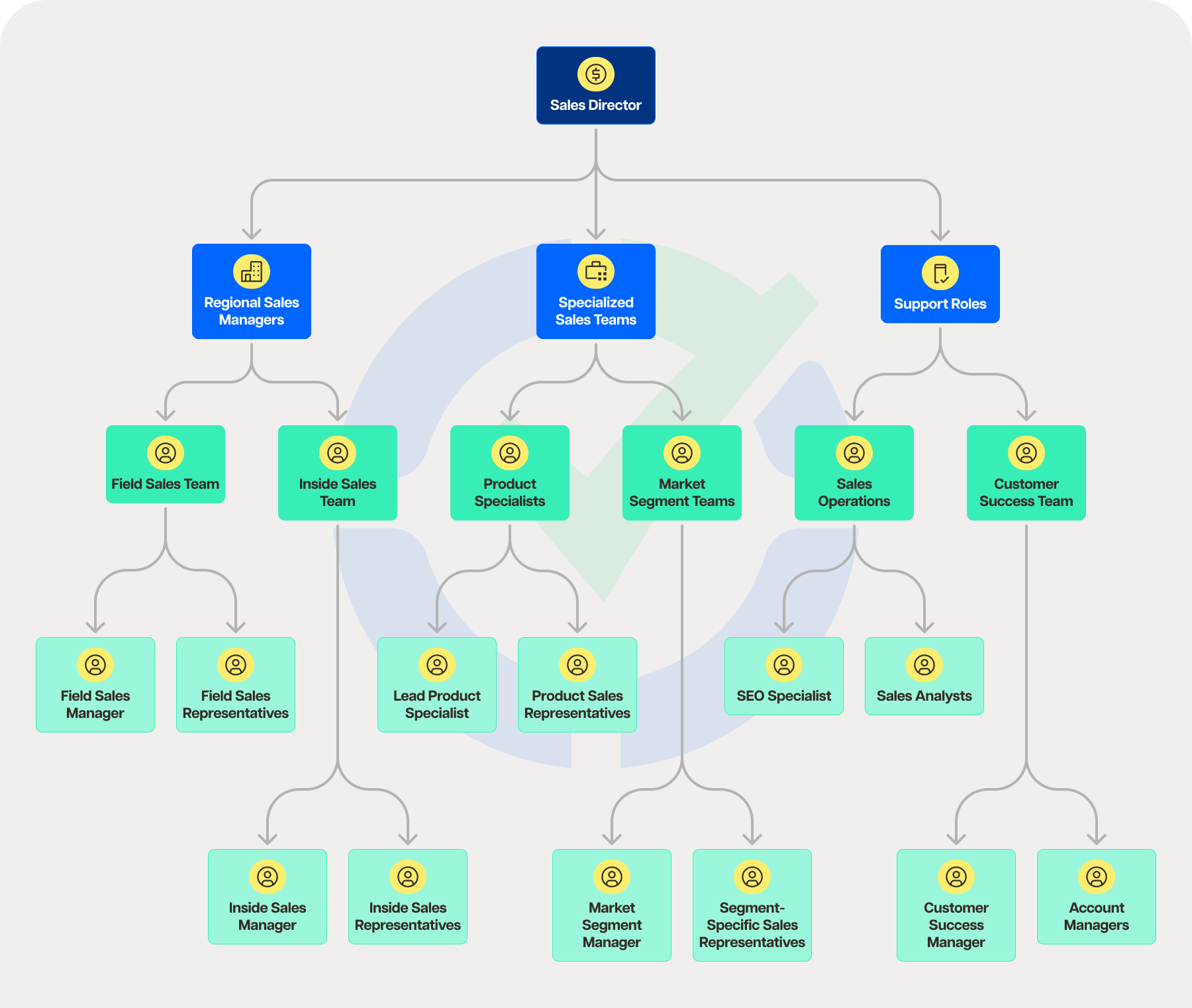
Sample sales team structure: Hybrid model
A hybrid sales team structure is a strategic amalgamation of different organizational models, tailored to meet the unique requirements of a business, adapt to fluctuating market conditions, and effectively serve diverse customer groups. This model excels in providing the sales force with the necessary flexibility, scalability, and specialization to drive success.
Text-based organization structure
Sales leadership
- Sales director: Leads the sales department, establishing strategic direction and objectives.
- Regional sales managers: Oversee sales activities within designated geographical areas, ensuring targets are met and strategies are effectively implemented.
Specialized sales teams
- Product specialists
- Lead product specialist: Serves as the primary expert for a specific product line, guiding the team.
- Product sales representatives: Specialize in selling and promoting the product line, leveraging in-depth knowledge and expertise.
- Market segment teams
- Market segment manager: Leads a team focused on a particular market segment or customer group, understanding and addressing their unique requirements.
- Segment-specific sales representatives: Dedicated to engaging with customers within their assigned segment, offering tailored solutions.
Support roles
- Sales operations
- Sales operations manager: Coordinates administrative, operational, and analytical support for the sales teams.
- Sales analysts: Focus on data analysis to enhance sales strategies and operations.
- Customer success team
- Customer success manager: Oversees initiatives aimed at ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty post-purchase.
- Account managers: Maintain and develop client relationships, fostering long-term engagement.
Cross-functional teams
- Inside sales team
- Inside sales manager: Leads the team responsible for remote sales activities, including lead generation and initial customer contacts.
- Inside Sales Representatives: Engage with prospects and customers over the phone or online, driving sales from a distance.
- Field sales team
- Field sales manager: Guides the team that conducts in-person sales activities, often dealing with complex sales cycles or high-value transactions.
- Field sales representatives: Specialize in face-to-face interactions, building relationships and closing deals outside the office.
This hybrid structure integrates the expertise of product and market specialists with the effectiveness of dedicated customer relationship and operational support roles. It allows for a versatile approach to sales, ensuring that all bases are covered from product knowledge to customer service.
Organizations can tweak the composition and focus of this structure to suit their specific objectives best, adapting to changes in the market and within their own team dynamics.
Designing the most efficient sales team structure
Assessing organizational requirements and goals, coordinating sales targets with company strategy, and striking a balance between flexibility and specialization are all necessary steps in building the most effective sales team structure. This results in a customized strategy that takes into account the organization’s unique demands, objectives, and competitive environment.
Implementing the structure
Metrics for assessing performance, productivity-boosting systems and tools, and training and development are necessary for effective implementation. This guarantees that the sales force is well-equipped, well-structured, and always evolving.
Conclusion
The effectiveness of a sales team’s organizational structure has a critical role in whether or not a company meets its revenue goals.
Businesses may develop a sales force that is not only productive but also flexible enough to adjust to shifting market conditions by comprehending various organizational structures, figuring out what makes a successful team, and creating a structure that supports those objectives.
Never forget that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer; the secret is to modify the framework to match your unique organizational requirements.

Andy is a technology & marketing leader who has delivered award-winning and world-first experiences.


